
History/origin: The name kilogram was derived from the French "kilogramme," which in turn came from adding Greek terminology meaning "a thousand," before the Late Latin term "gramma" meaning "a small weight." The changes were intended to improve the definitions of SI base units, not to actually change how the units are used throughout the world. Even though the definition of the kilogram was changed in 2019, the actual size of the unit remained the same. The meter and the second are defined in terms of c, the speed of light, and cesium frequency, Δ νCs. It is currently defined based on the fixed numerical value of the Planck constant, h, which is equal to 6.62607015 × 10 -34 in the units of J Kilogramĭefinition: A kilogram (symbol: kg) is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI). Standards on the nutrition labels of food products often require the relative contents to be stated per 100 grams of the product. For example, the gram is typically used to measure non-liquid ingredients used for cooking or groceries.
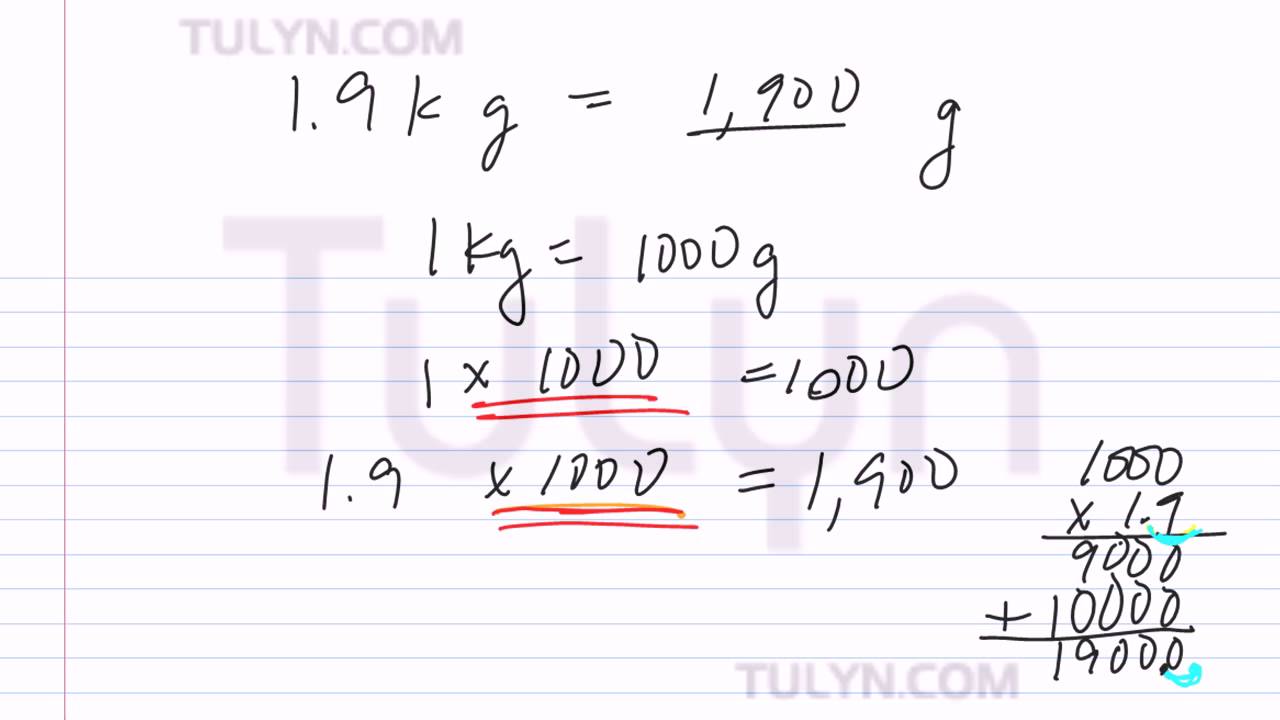
The gram was later redefined as one thousandth of a kilogram, the SI (meter-kilogram-second system of units) base unit of mass.Ĭurrent use: The gram is widely used in every life as well as scientific contexts.

The gram used to be a fundamental unit of mass as part of centimeter-gram-second systems of units up until the widespread adoption of SI, which uses kilograms as the base unit of mass. History/origin: Originally, a gram was defined as the absolute weight of pure water in a cubic centimeter at the temperature of melting ice (later 4 ☌). Since 2019, the definition of the kilogram is no longer based on the international prototype, and rather is based on Planck's constant, h, along with the new definitions of the second and the meter. The definition of the gram is based on the kilogram, where a gram is one thousandth of a kilogram, the SI base unit of mass. Definition: A gram (symbol: g) is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
